Adiabatic Lapse Rate, Dry
from the first law of thermodynamics
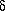 W = n · cv dT + P dV = 0
W = n · cv dT + P dV = 0where cv is given in units of erg/K/mole and n is the number of moles. The derivative of the ideal gas law, P · V = n R T, is
equating P dV and noting that R = cp - cv yields
Cp = cp/<mw> and
 = n · <mw>/V so that
= n · <mw>/V so that )
)From hydrostatic equilibrium and the gas law we can convert from pressure to height coordinates:
 dz
dz a
a  -dT/dz|a = g/Cp
-dT/dz|a = g/Cp
<g> cm/s2 | Cp J/gm/K | Adiabatic Lapse Rate K/Km | Rg J/gm/K | Autoconvective Lapse Rate K/Km | |
| Venus | 889.89 | 0.8501 | 10.468 | 0.18892 | 47.104 |
| Earth | 979.86 | 1.0040 | 9.760 | 0.28710 | 34.130 |
| Mars | 374.10 | 0.8312 | 4.500 | 0.18892 | 19.802 |
| Jupiter | 2425.61 | 12.3591 | 1.963 | 3.74518 | 6.477 |
| Saturn | 1000.09 | 14.0129 | 0.714 | 3.89246 | 2.569 |
| Uranus | 880.07 | 13.0137 | 0.676 | 3.61491 | 2.435 |
| Neptune | 1110.46 | 13.0137 | 0.853 | 3.61491 | 3.072 |
| Titan | 135.80 | 1.0440 | 1.301 | 0.29000 | 4.683 |
 PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
