Credit NASA
Description
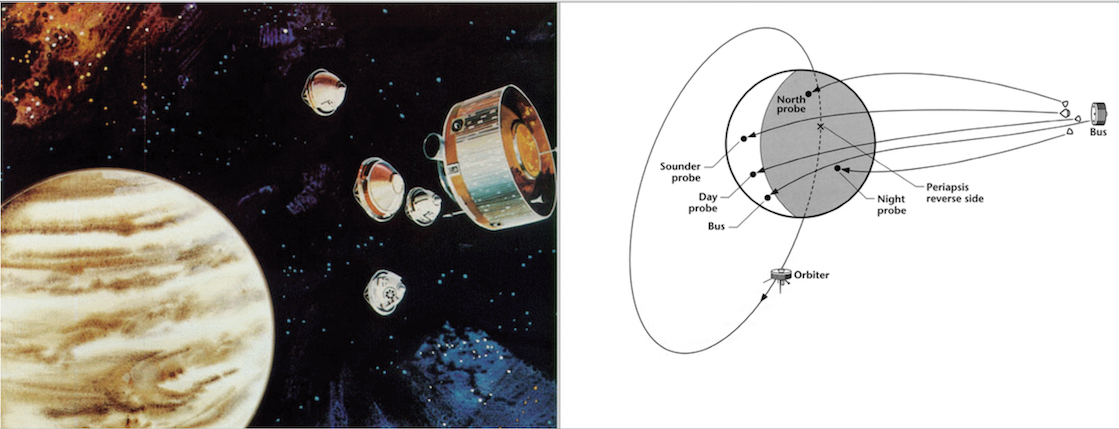
The Pioneer Venus Mission consisted of two major parts: the Multiprobe and the Orbiter. The Multiprobe was composed of the carrier or Bus (290 kg), a large Sounder probe (315 kg), and 3 smaller probes (90 kg each). It was launched on August 8, 1978. The multiprobe reached Venus on December 9,1978 and the large probe was released on November 15.
As the four probes descended, the Pioneer Venus Probe Bus followed a well-defined ballistic trajectory above the atmosphere that was accurately known with respect to the planet's surface. Probe velocities were measured relative to the Bus. Additionally, four ground stations on Earth simultaneously tracked the four probes at 2291 to 2293 MHz and received signals from all four probes and the bus simultaneously. The Doppler frequency shifts of the received 13 cm (S-band) signals gave the component of the velocity vector along the Earth-spacecraft line of sight. The differential long-baseline interferometry was used to find the other two components of the velocity vector of each probe.
Reference
Shapiro, I. I., Miller, R. B., Smith, J. R, Ramos, R., and Liebrecht, P., Wind velocities on Venus: Vector determination by radio interferometry, Science, 203, No. 4382, 805-806, doi:10.1126/science.203.4382.805, Feb. 1979.
Accessing the Data
Bundle Pioneer Venus Multiprobe DLBI Relative Crustal and Atmospheric Velocity Components Data Bundle
User’s guide
Derived Data
Citation
PDS recommendations for citing data sets can be found here.
Won, Y.-I., S.A. McLaughlin, C.C. Councilman III (2025). Pioneer Venus Multiprobe DLBI Relative Crustal and Atmospheric Velocity Components Data Bundle, NASA Planetary Data System, http://www.doi.org/10.17189/kzg5-ep44.
 PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node