- A radio occultation of Saturn
- UV and IR spectra of the atmosphere
- A futile effort to image surface features and cloud dynamics
- A search for a magnetic field
- Studies of the of Titan’s interaction with the solar wind and Saturn’s magnetosphere

Introduction
The two Voyager spacecraft were equipped with an enabling scan platform, a challenging limited computer and eight-track digital tape recorder. The dual spacecraft mission was designed to take advantage of a planetary alignment that occurs every 175 years. Although Voyager’s goal was to explore Jupiter and Saturn and their environments, different options were reserved for the 2 crafts. Voyager 1 was targeted to Jupiter, Saturn and Titan while the Voyager 2 trajectory allowed it to continue on to Uranus and Neptune.
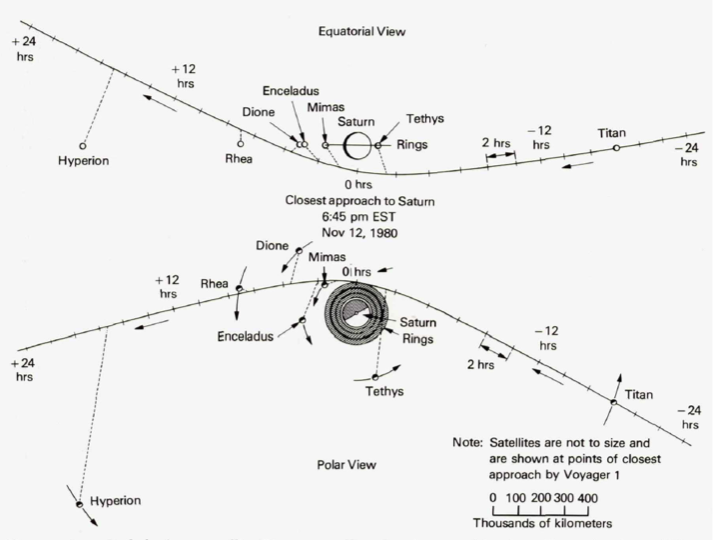
The Voyager 1 encounter with Titan spanned the time period between 1980-08-27 to 1980-11-15 with closest approach occurring at 1980-11-11 at 9:41 at a distance of 6490 km from the planet. The Voyager 1 radio occultation experiment began at 10:45.
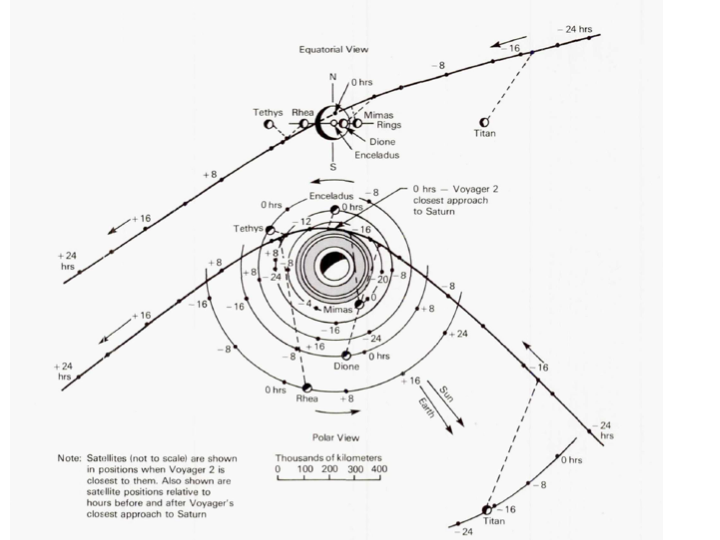
The less favorable Voyager 2 closest approach was at 666,190 km and the encounter spanned the period from1981-06-24 to 1981-08-25.
Titan Achievements
Among the Voyager observations at Titan were:
References
Voyages to Saturn NASA SP-451 1982
See Space Sciences Reviews Volume 21 Issue 2, Nov. 1977 for details on instrumentation
Lindal, G.F., et al., The atmosphere of Titan: An analysis of the Voyager 1 radio occultation measurements, Icarus, Volume 53, Issue 2, p. 348-363, DOI 10.1016/0019-1035(83)90155-0
Kunde, V.G., et al C4H2, HC3N and C2N2 in Titan's Atmosphere, Nature, 292, 686-688, 1981.
Useful Documents
Mission Overview
Spacecraft Description
Voyager 1
Voyager 2
A list of pertinent references
Also See Space Science Reviews 21 (1977 – Issue 2) 77-101
Understanding the Instruments and Archived Data
ISS - Narrow and wide angle cameras with filters in a 280-640 nm range (red blind)
IRIS - Infrared Interferometric Spectrometer
UVS - Ultraviolet Spectrometer
PPS - Photopolarimeter
MAG - Triaxial Fluxgate Magnetometer
LECP - Low Energy Charged Particle Detector
PLS - Plasma Spectrometer
PRA - Planetary Radio Astronomy Investigation
PWS - Planetary Wave Spectrometer
CRS - Cosmic Ray System
RSS - Radio Science System
IRIS - Infrared Interferometric Spectrometer
UVS - Ultraviolet Spectrometer
PPS - Photopolarimeter
MAG - Triaxial Fluxgate Magnetometer
LECP - Low Energy Charged Particle Detector
PLS - Plasma Spectrometer
PRA - Planetary Radio Astronomy Investigation
PWS - Planetary Wave Spectrometer
CRS - Cosmic Ray System
RSS - Radio Science System
Other Useful Products for Interpreting the Data
Locating Voyager Publications
Geometry in "SPICE" format may be obtained at the NAIF node
 PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node