Each of the 3-axis spin stabilized Voyager spacecraft was equipped with an enabling scan platform, a challenging limited computer and eight-track digital tape recorder. The mission was designed to take advantage of a planetary alignment that occurs every 175 years. Although Voyager’s goal was to explore Jupiter and Saturn and their environments, different options were reserved for the 2 crafts. Voyager 1 was targeted to Jupiter, Saturn and Titan while the Voyager 2 trajectory allowed it to continue on to Uranus and Neptune.
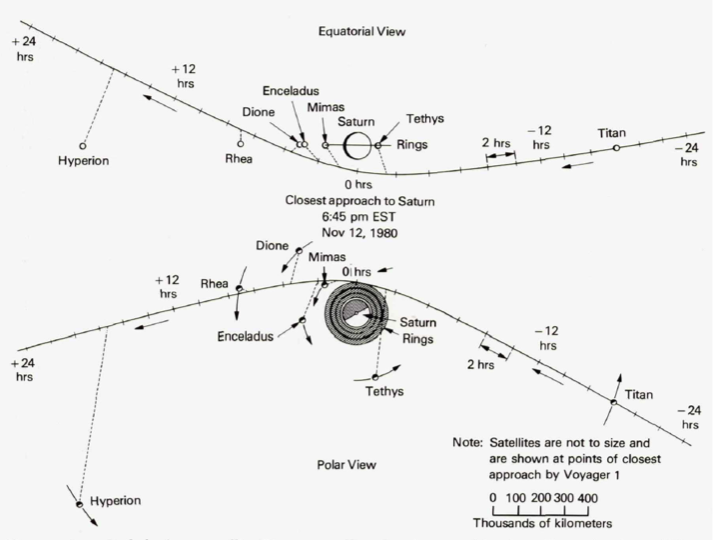
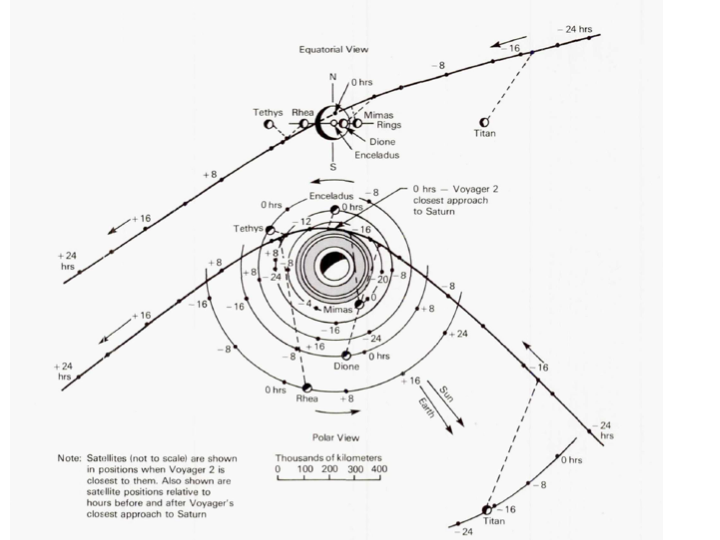
The Voyager 1 encounter spanned the time period between 1980-08-22 and 1980-12-14 with closest approach on November 12, 1980 at a distance of 184,300 km from the planet center. While the Voyager 2 encounter spanned 1980-12-14 to 1981-09-03 with closest approach on August 25,1981 at a distance of 161,000 km from the planet center
Voyager's objective was the exploration of Jupiter and Saturn, and their magnetospheres and satellites. Major emphasis was placed on studying the satellites in as much detail as possible. The study of Titan, the only satellite in the solar system known to have an extensive atmosphere, was nearly as high a priority as studies of Saturn itself
Saturn Achievements
Voyages to Saturn NASA SP-451 1982 provides a review on the Voyage 1 and 2 encounters and summarizes the insights gained from the mission.
References Helpful in Scoping the Mission
Mission Overview
Spacecraft Description A list of pertinent references
Also See Space Science Reviews 21 (1977 – Issue 2) 77-101
Spacecraft Description A list of pertinent references
Also See Space Science Reviews 21 (1977 – Issue 2) 77-101
Understanding the Instruments and Archived Data
ISS - Narrow and wide angle cameras with filters in a 280-640 nm range
IRIS - Infrared Interferometric Spectrometer
UVS - Ultraviolet Spectrometer
PPS - Photopolarimeter
MAG - Triaxial Fluxgate Magnetometer
LECP - Low Energy Charged Particle Detector
PLS - Plasma Spectrometer
PRA - Planetary Radio Astronomy Investigation
PWS - Planetary Wave Spectrometer
CRS - Cosmic Ray System
RSS - Radio Science System
IRIS - Infrared Interferometric Spectrometer
UVS - Ultraviolet Spectrometer
PPS - Photopolarimeter
MAG - Triaxial Fluxgate Magnetometer
LECP - Low Energy Charged Particle Detector
PLS - Plasma Spectrometer
PRA - Planetary Radio Astronomy Investigation
PWS - Planetary Wave Spectrometer
CRS - Cosmic Ray System
RSS - Radio Science System
Other Useful Products for Interpreting the Data
Locating Voyager Publications
Geometry in "SPICE" format may be obtained at the NAIF node
 PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node