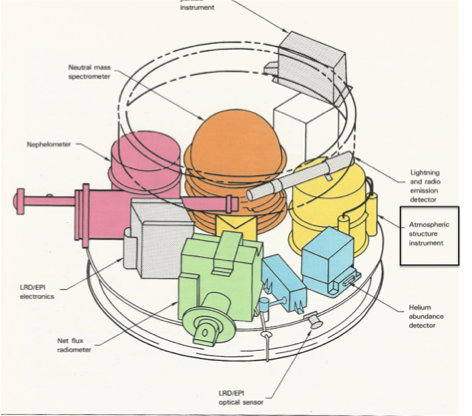
The Galileo Probe Atmospheric Structure Instrument (ASI) measured state properties of Jupiter's atmosphere from nanobar pressure levels to a final pressure of ~24 bars. The depth reached in the probe's parachute descent, calculated from measured temperatures and pressures assuming hydrostatic equilibrium, was ~160 km or 0.22% of the radius of Jupiter. Velocities during descent decreased from ~400 m/s at parachute deployment to 156 m/s in the first 100 s, to ~48 m/s at the 3-bar level, and to ~30 m/s at loss of signal.
Access to the Galileo Probe Data Volume
Citing the data
Publications - A listing of team members to facilitate literature searches.
References Helpful in Scoping the Mission
The Atmospheric Structure Instrument Data
Review Article
Instrument Description
The Data set Overview
An Explanation of the data
The Data Files
Instrument Description
The Data set Overview
An Explanation of the data
The Data Files
Other Documentation
Access to the Galileo Probe Data Volume
PDS recommendations for citing data sets can be found here.
Knight, Tony, (1996), Galileo Probe ASI Raw Data Archive, PDS Atmospheres (ATM) Node, https://doi.org/10.17189/tfsa-pb91
Knight, Tony, (1996), Galileo Probe ASI Raw Data Archive, PDS Atmospheres (ATM) Node, https://doi.org/10.17189/tfsa-pb91
Publications - A listing of team members to facilitate literature searches.
 PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node