Spacecraft and Mission Description
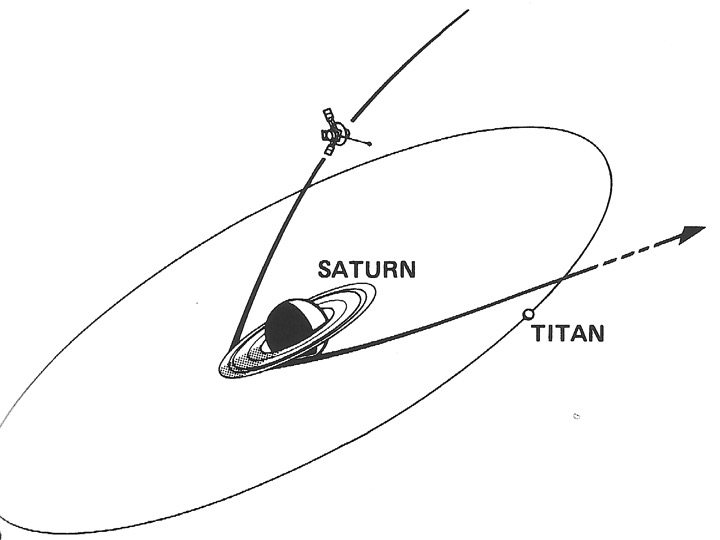
Pioneer 11 was launched on April 5, 1973 using the Atlas/Centaur/TE364-4 launch vehicle. The Saturn encounter began on April 2, 1979. The ensuing encounter involved a trajectory such that on September 1, 1979 the spacecraft passed through the ring plane at a distance of 35,400 km of the outer edge of the A Ring and swung under the rings, passing within 21,400 km of the cloud-tops. After passing Saturn the craft came within 355,000 km of Titan. The inclination of the spacecraft trajectory relative to the ring plane was 6.6°.
The Pioneer spacecraft were lightweight spin-stabilized craft powered by SNAP-19 type radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). The high-gain antenna was 2.74 m in diameter, The two radio transmitters each produced 8 W of transmitted power at S-band.
The Pioneer 11 Mission ended on 30 September 1995, when the last transmission from the spacecraft was received. The spacecraft is headed toward the constellation of Aquila (The Eagle), Northwest of the constellation of Sagittarius. Pioneer 11 will pass near one of the stars in the constellation in about 4 million years.
Pioneer 11 Saturn Discoveries
Established the existence of and quantified Saturn’s magnetic field. (note: the alignment of the field with Saturn's rotational axis does not provide a signature that could be detected by earth-based observers.)
Set limits on ring-moon structure
Obtained photometric and polarization measurements of Titan over a wide range of phase angles.
Refined the gravity field of Saturn and obtained better value of the oblateness value and a measure of the ratio of emitted to absorbed energy.
Obtained constraints on the structure of Saturn’s atmosphere
Accessing the data
Note: The Pioneer Missions were carried out before effective processes for archiving were in place. As a result documentation of the mission is incomplete and some data is missing. A NASA special report, designed for the general public may fill in some of the missing information.
Mission Description (See P11_MISSION.CAT)
Spacecraft Description (See P11_INST_HOST.CAT)
Understanding the Instruments and Archived Data
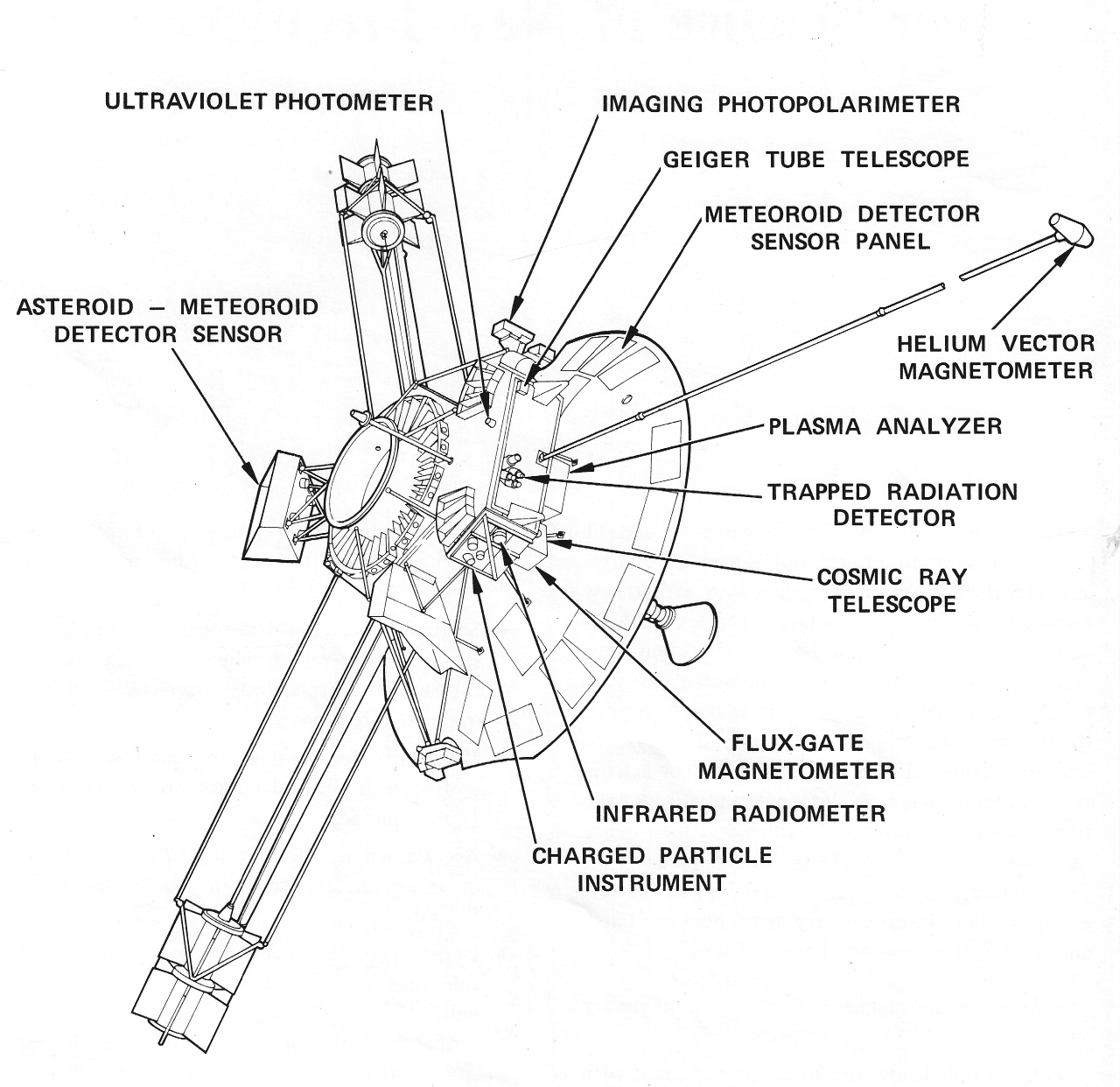
UV - Ultraviolet Photometer
IPP - Imaging Photopolarimeter See publications. See NASA Special Report – NASA SP 446
PA - Plasma Analyzer Pioneer 11
TRD - Trapped Radiation detector Pioneer 11
FGM - Flux-Gate Magnetometer Pioneer 11
HVM - Helium Vector Magnetometer Pioneer 11
CPI - Charged Particle Instrument Pioneer 11
GTT - Geiger Tube Telescope – See publications
CRT - Cosmic Ray Telescope - See publications
AMD - Asteroid Meteoroid Detector – No data – See publications for references
POS - Spacecraft Position - See publications
Other Useful Products for Interpreting the Data
Publications – A listing of team members to facilitate literature searches.
 PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node